
동의어 Synonym
- 사고 트라이앵글 Accident Triangle
- 하인리히 법칙 Heinrich's Law
- 하인리히 사고 피라미드 Heinrich's Accident Pyramid
- 하인리히 사고 트라이앵글 Heinrich’s Accident Triangle
- 버드의 트라이앵글 Bird’s Triangle
- 1:29:100의 법칙 1:29:100 Law
- 1:30:100의 법칙 1:30:100 Law
정의 Definition
하인리히의 법칙은 산업 재해 예방에 대한 이론이다.
Heinrich’s law is a theory of industrial accident prevention.
사건 발생(occurrence) 및 더 심각한 사건(incident) 및 사고(accident)의 관계에 대해 보통 트라이앵글이나 피라미드 그림으로 나타낸다.
It normally shows as a pictorial description, a pyramid, or a triangle, of the relationship between near misses(occurrences) and more serious incidents(minor accidents) and accidents.

최초 제안 First Proposal

*Source: https://alchetron.com/Herbert-William-Heinrich
Herbert William Heinrich
- 1930년대 미국 산업 안전의 선구자 American industrial safety pioneer from the 1930s
- 1886년 10월 8일 ~ 1962년 6월 22일 October 6, 1886 – June 22, 1962
- 미국 버몬트 주 베닝턴 출생 Born in Bennington, Vermont, U.S.
1931년 하인리히(Herber William Heinrich)의 저서 “산업 재해 예방에 대한 과학적 접근(Industrial Accident Prevention, A Scientific Approach)”에서 그는 하인리히의 법칙으로 알려지게 되는 아래와 같은 개념을 제언했다.
In his 1931 book "Industrial Accident Prevention, A Scientific Approach", Herbert William Heinrich put forward the following concept that became known as Heinrich's Law:
작업 현장에서 ‘중상’을 유발하는 사고 ‘1건’에 대해
‘경상’을 입은 사고는 ‘29건’,
‘부상을 입히지 않은 사고’는 ‘300건’이 존재한다.
in a workplace,
for every accident that causes a major injury,
there are 29 accidents that cause minor injuries
and 300 accidents that cause no injuries.

그가 책을 출간했을 때 그는 여행자 보험 회사에서 엔지니어링 및 감사 부서의 부관리자였다.
He was an Assistant Superintendent of the Engineering and Inspection Division of Travelers Insurance Company when he published his book.
그는 보험 회사의 파일뿐만 아니라 개별 산업 현장의 기록에서 75,000건 이상의 사고 보고서에 대한 연구를 하였고, 이 데이터들에서 1건의 주요 부상 사고와 29건의 경미한 부상 사고, 300건의 부상 없는 사고의 관계를 제안하게 됩니다. 그는 경미한 사고 건수를 줄임으로써 산업체들이 대형 사고 건수의 상관관계를 볼 것이라는 결론을 도출하기에 이른다.
He commenced a study of more than 75,000 accident reports from the insurance company's files as well as records held by individual industry sites. From this data, he proposed a relationship of one major injury accident to 29 minor injury accidents, to 300 no-injury accidents. He drew the conclusion that, by reducing the number of minor accidents, industrial companies would see a correlating fall in the number of major accidents.
하인리히의 이론은 또한 모든 사고의 88%가 안전하지 않은 행동을 수행하려는 인간의 결정으로 인해 발생한다고 제안했다.
Heinrich's theory also suggested that 88% of all accidents were caused by a human decision to carry out an unsafe act.
발전 Development
이는 프랭크 E 버드를 비롯한 여러 사람에 의해 업데이트되고 확장되었다.
Triangle has since been updated and expanded upon by other writers, notably Frank E. Bird.
1966년 프랭크 E 버드에 의해 거의 300개 회사의 170만 건의 사고 보고서를 분석한 결과 더 발전되었다.
The theory was developed further by Frank E Bird in 1966 based on the analysis of 1.7 million accident reports from almost 300 companies.
그는 하나의 심각한 부상 사고와 10개의 경미한 부상(응급 치료 전용) 사고, 30개의 피해를 야기하는 사고, 600개의 니어미스 사이의 관계를 보여주는 수정된 삼각형을 제작하였다.
He produced an amended triangle that showed a relationship of one serious injury accident to 10 minor injury (first aid only) accidents, to 30 damage-causing accidents, to 600 near misses.
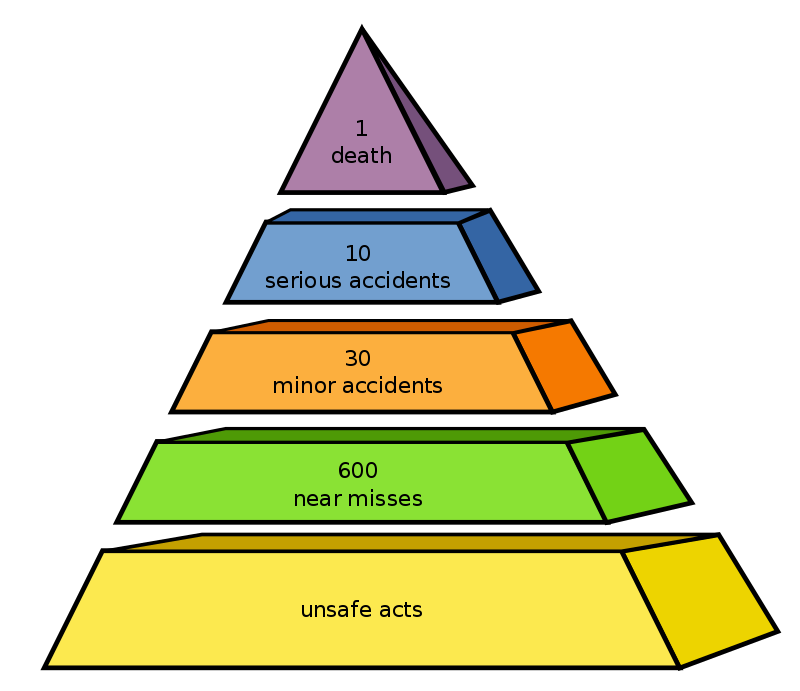
그 값들은 1974년 A.D. Swain의 연구, The Human Element in Systems Safety, 에 의해 증명되었다.
The numbers used by Bird were confirmed by a 1974 study by A. D. Swain, entitled The Human Element in Systems Safety.
버드는 보고된 니어미스의 수와 대형사고의 수 사이의 관계를 보여주었고, 대부분의 사고는 적절한 개입에 의해 예측되고 예방될 수 있다고 주장했다.
The bird showed a relationship between the number of reported near misses and the number of major accidents and claimed that the majority of accidents could be predicted and prevented by appropriate intervention.
특징 Characteristics
- 하인리히의 법칙은 확률에 기초하며 사건들의 수가 심각성에 반비례함을 추정한다.
Heinrich's law is based on probability and assumes that the number of accidents is inversely proportional to the severity of those accidents. - 이는 경미한 사건의 수를 최소화하면 심각한 사고를 줄일 수 있다는 결론에 도달한다.
It leads to the conclusion that minimizing the number of minor incidents will lead to a reduction in major accidents. - 일반적으로 피라미드로 묘사되고 단순성을 위해 ‘경미한 사건 수’가 ‘30’으로 표시된다.
This is commonly depicted as a pyramid or a triangle (in this case with the number of minor incidents shown as 30 for simplicity).
긍적적인 평가 Positive Comments
- 산업 보건 및 안전 프로그램에 널리 사용되고 있다.
The triangle has been widely used in industrial health and safety programs. - 20세기 직장 건강과 안전 철학의 초석으로 묘사된다.
It has been described as a cornerstone of 20th-century workplace health and safety philosophy. - 일부 전문가들에 의해 행동 기반 안전 관리(BBS) 이론의 기초라고 주장된다.
It is claimed as the basis for the theory of behavior-based safety(BBS) by some experts in this field. - 피라미드는 개인이 근본 원인을 좁히고 위험이나 원인을 제거하거나 통제할 수 있게 한다.
The pyramid allows individuals to narrow down the root cause and eliminate or control the hazard or cause.
부정적인 평가/비판 Negative Comments/Critism
- 모든 경미한 부상과 실수가 보고되지 않을 것이며, 이는 삼각형의 일부 결함을 초래할 수 있다.
One could assume that not all minor injuries and near misses will be reported, which will result in some fault of the triangle. - 1998년 연구에 따르면 좁고 사방이 막힌 공간에서는 심각한 부상이나 사망에 대해 1.2개의 경미한 부상을 입었다.
A 1998 study showed that in confined spaces the relationship was significantly different: 1.2 minor injuries for each serious injury or death.
* McManus, Neil (1998). Safety and Health in Confined Spaces. CRC Press. p. 6. ISBN 9781566703260. Retrieved 18 November 2018.
- 1990년대 중반 영국의 사고 데이터에 대한 광범위한 연구에서는 한 명의 사망자에 대해 207명의 심각한 부상과 1,402명의 전치 3일 이상의 부상, 2,754명의 경미한 부상이라는 결론이 나타났다.
A broad study of UK accident data in the mid-1990s showed a relationship of 1 fatality to 207 major injuries, to 1,402 injuries causing three or more days lost time injuries, to 2,754 minor injuries.
* Health and Safety Executive (1999). The cost to Britain of workplace accidents and work-related ill health in 1995/96 (PDF). p. 32. ISBN 978-0-7176-1709-8. Retrieved 18 November 2018.
- 석유 및 가스 산업과 관련된 2010년 보고서는 큰 데이터 셋과 광범위한 활동에 적용될 때만 원래의 가치가 사실로 유지됨을 보여주었다.
A 2010 report relating to the oil and gas industry showed that the original values held true only when applied to a large dataset and a broad range of activities.
* Anderson, Martin; Denkl, Michael (2010). "The Heinrich Accident Triangle – Too Simplistic A Model For HSE Management in The 21st Century?". SPE International Conference on Health, Safety and Environment in Oil and Gas Exploration and Production. Society of Petroleum Engineers. doi:10.2118/126661-MS. Retrieved 18 November 2018. - 하인리히의 원본 파일이 유실되어 그가 사용한 사고 수에 대해 현재 입증 불가능하다.
Heinrich's original files have since been lost so his accident figures cannot be proven.
* Johnson, Ashley (1 October 2001). "Examining the foundation". Safety & Health. National Safety Council Congress & Expo. Retrieved 18 November 2018. - 에드워즈 데밍(W. Edwards Deming)은 인간의 행동을 직장에서 일어나는 대부분의 사고의 원인으로 간주하는 하인리히의 이론은 부정확하며, 실제로 사고의 대부분을 야기한 것은 형편없는 관리 시스템이었다고 말했다.
W. Edwards Deming stated that Heinrich's theory attributing human action as the cause of most accidents in the workplace was incorrect and it was, in fact, poor management systems that caused the majority of accidents.
* Johnson, Ashley (1 October 2001). "Examining the foundation". Safety & Health. National Safety Council Congress & Expo. Retrieved 18 November 2018. - 이것이 경미한 사고 감소에만 관심을 집중한다는 비판도 존재한다. 이는 직장의 감독자들이 더 빈번하지만 덜 심각한 위험의 가능성을 줄이는 데 초점을 맞추기 위해 일을 계획할 때, 더 심각하지만 일어날 가능성이 적은 위험을 무시하도록 만들었다고 주장한다. 2010년 석유 및 가스 연구에서는 이러한 태도가 경미한 사고가 크게 줄었음에도 불구하고 지난 5년에서 8년 동안 해당 산업의 사망자 감소 효과가 없었음을 주장한다.
There has been criticism of the triangle for focusing attention on the reduction of minor accidents. It has been claimed that this has led to workplace supervisors to ignore more serious but less likely risks when planning works in order to focus on reducing the likelihood of more common but less serious risks. The 2010 oil and gas study claimed that attitude had led to a halt in the reduction of fatalities in that industry in the preceding five to eight years, despite a significant reduction in minor accidents.
* Anderson, Martin; Denkl, Michael (2010). "The Heinrich Accident Triangle – Too Simplistic A Model For HSE Management in The 21st Century?". SPE International Conference on Health, Safety and Environment in Oil and Gas Exploration and Production. Society of Petroleum Engineers. doi:10.2118/126661-MS. Retrieved 18 November 2018.
끝.
The End.
'Engineering > Quality Engineering' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 카노 모델 Kano Model (1) | 2022.08.23 |
|---|---|
| 겜바 워크 Gemba Walk / 겐바 워크 Genba Walk (0) | 2022.08.19 |
| 생존 편향 Survivorship bias (0) | 2022.08.09 |